


 7.1 Software Service Aids
Package
7.1 Software Service Aids
Package


 7.1 Software Service Aids
Package
7.1 Software Service Aids
Package
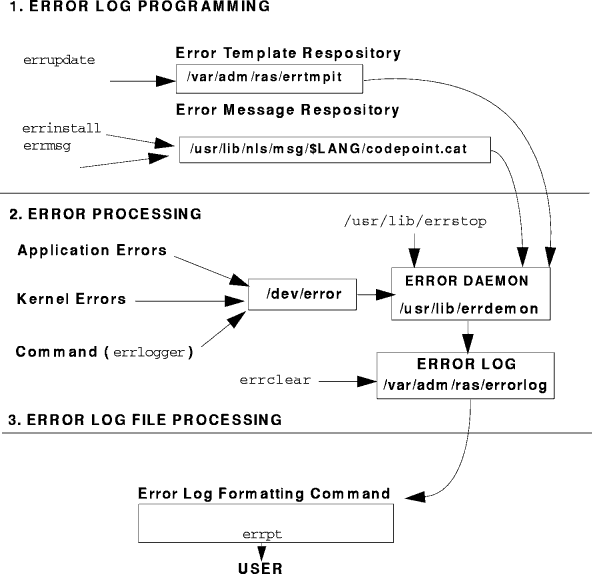
The error logging facility records hardware and software failures in the error log for informational purposes or for fault detection and corrective action. The error logging subsystem is composed of three components whose processing flow is shown in Figure 92. The type of tasks are defined as follows.
The following sections discuss various error log management related functions.
This section discusses the use of errdemon command to customize the error log file.
# /usr/lib/errdemon -l Error Log Attributes -------------------------------------------- Log File /var/adm/ras/errlog Log Size 4096 bytes Memory Buffer Size 8192 bytes
The preceding example shows the default error log file attributes. The log file size cannot be made smaller than the hard-coded default of 4 KB and the buffer cannot be made smaller than the hard-coded default of 8 KB.
/usr/lib/errdemon -i /var/adm/ras/errlog.test
/usr/lib/errdemon -s 8192
If the log file size specified is smaller than the size of the log file currently in use, the current log file is renamed by appending .old to the file name and a new log file is created with the specified size limit. The amount of space specified is reserved for the error log file and is not available for use by other files. Therefore, you should be careful not to make the log excessively large. But, if you make the log too small, important information may be overwritten prematurely. When the log file size limit is reached, the file wraps. That is, the oldest entries are overwritten by new entries.
# /usr/lib/errdemon -B 16384 0315-175 The error log memory buffer size you supplied will be rounded up to a multiple of 4096 bytes.
If the specified buffer size is larger than the buffer size currently in use, the in-memory buffer is immediately increased and if the specified buffer size is smaller than the buffer size currently in use, the new size is put into effect the next time the error daemon is started after the system is rebooted. The size you specify is rounded up to the next integral multiple of the memory page size (4 KB).
You should be careful not to impact your system's performance by making the buffer excessively large. But, if you make the buffer too small, the buffer may become full if error entries are arriving faster than they are being read from the buffer and put into the log file. When the buffer is full, new entries are discarded until space becomes available in the buffer. When this situation occurs, an error log entry is created to inform you of the problem.
The following command shows the new attributes of error log file.
# /usr/lib/errdemon -l Error Log Attributes -------------------------------------------- Log File /var/adm/ras/errlog.test Log Size 8192 bytes Memory Buffer Size 16384 bytes
To determine if error logging daemon is on or off,
issue the errpt command. The errpt command output may contain
entries as shown in Figure 93.

Figure 93: errpt Command
If the errpt command does not generate entries, error logging has been turned off. To activate the daemon use the following command.
/usr/lib/errdemon
The errdemon daemon starts error logging and writes error log entries in the system error log.
To stop the error logging daemon from logging entries use the following command.
/usr/lib/errstop
Cleaning of the error log implies deleting old or unnecessary entries from the error log. Cleaning is normally done as part of the daily cron command execution (see Chapter 14. The cron Daemon and crontab for more information on cron). If it is not done automatically, you should probably clean the error log regularly.
To delete all the entries from the error log, use the following command:
errclear 0
To selectively remove entries from the error log, for example, to delete all software errors enteries use the following command:
errclear -d S 0
Alternatively, use the SMIT fast path command (smit errclear) that
will display the screen as shown in Figure 94 and enter
appropriate fields as per requirement to clean the error log.
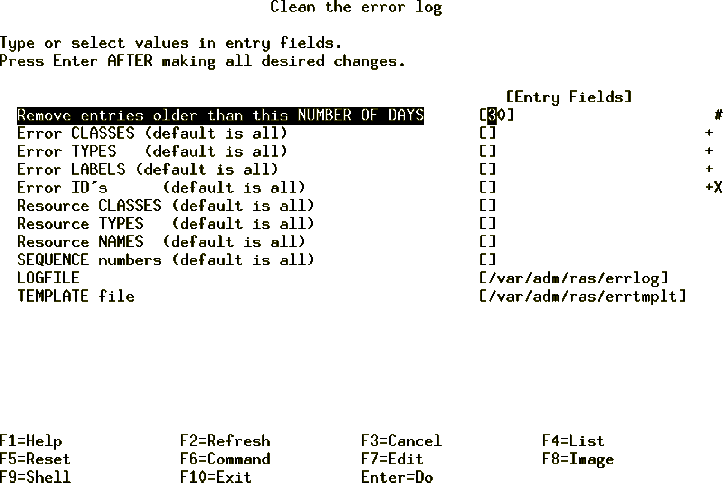
Figure 94: SMT errclear Command
The errpt command generates the default summary error report that contains one line of data for each error. It includes flags for selecting errors that match specific criteria. By using the default condition, you can display error log entries in the reverse order they occurred and were recorded. By using the - c (concurrent) flag, you can display errors as they occur. You can use flags to generate reports with different formats. Following is the syntax of the errpt command.
errpt [ -a ] [ -c ] [ -d ErrorClassList ] [ -e EndDate ] [ -g ] [ -i File ] [ -j ErrorID [ ,ErrorID ] ] | [ -k ErrorID [ ,ErrorID ] ] [ -J ErrorLabel [ ,ErrorLabel ] ] | [ -K ErrorLabel [ ,ErrorLabel ] ] [ -l SequenceNumber ] [ -m Machine ] [ -n Node ] [ -s StartDate ] [ -F FlagList ] [ -N ResourceNameList ] [ -R ResourceTypeList ] [ -S ResourceClassList ] [ -T ErrorTypeList ] [ -y File ] [ -z File ]
The output of errpt command without any flag will display the error log enteries with the following fields.
Using errpt command without a flag will output all the enteries in the log as shown in the following example. Since the number of error log enteries may exceed a single page, you can use errpt|pg pipe to have a page-wise view.
# errpt IDENTIFIER TIMESTAMP T C RESOURCE_NAME DESCRIPTION 0BA49C99 1106154298 T H scsi0 SCSI BUS ERROR E18E984F 1106110298 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR 2A9F5252 1106094298 P H tok0 WIRE FAULT E18E984F 1102120498 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR E18E984F 1101105898 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR AD331440 1101104498 U S SYSDUMP SYSTEM DUMP E18E984F 1030182798 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR E18E984F 1030182698 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR E18E984F 1030182598 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR E18E984F 1023175198 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR E18E984F 1023175098 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR E18E984F 1023174898 P S SRC SOFTWARE PROGRAM ERROR 2A9F5252 1022143498 P H tok0 WIRE FAULT 35BFC499 1022081198 P H hdisk0 DISK OPERATION ERROR AD331440 1021185998 U S SYSDUMP SYSTEM DUMP 0BA49C99 1021185798 T H scsi0 SCSI BUS ERROR 35BFC499 1021180298 P H hdisk0 DISK OPERATION ERROR
The preceding example shows that the resource name for a disk operation error is hdisk0. To obtain all the errors with resource name hdisk0 from the error log, use the errpt command with -N flag as shown in the following example:
# errpt -N hdisk0 IDENTIFIER TIMESTAMP T C RESOURCE_NAME DESCRIPTION 35BFC499 1022081198 P H hdisk0 DISK OPERATION ERROR 35BFC499 1021180298 P H hdisk0 DISK OPERATION ERROR
To read the contents of an error log report, use the errpt command with the -a flag. For example, to read an error log report with resource name hdisk0, use the errpt command with the -a and -j flags with error identifier as shown in the following sample error report:
# errpt -a -j 35BFC499
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
LABEL: DISK_ERR3
IDENTIFIER: 35BFC499
Date/Time: Thu Oct 22 08:11:12
Sequence Number: 36
Machine Id: 006151474C00
Node Id: sv1051c
Class: H
Type: PERM
Resource Name: hdisk0
Resource Class: disk
Resource Type: scsd
Location: 04-B0-00-6,0
VPD:
Manufacturer................IBM
Machine Type and Model......DORS-32160 !#
FRU Number..................
ROS Level and ID............57413345
Serial Number...............5U5W6388
EC Level....................85G3685
Part Number.................07H1132
Device Specific.(Z0)........000002028F00001A
Device Specific.(Z1)........39H2916
Device Specific.(Z2)........0933
Device Specific.(Z3)........1296
Device Specific.(Z4)........0001
Device Specific.(Z5)........16
Description
DISK OPERATION ERROR
Probable Causes
DASD DEVICE
STORAGE DEVICE CABLE
Failure Causes
DISK DRIVE
DISK DRIVE ELECTRONICS
STORAGE DEVICE CABLE
Recommended Actions
PERFORM PROBLEM DETERMINATION PROCEDURES
Detail Data
SENSE DATA
0A06 0000 2800 0000 0088 0002 0000 0000 0200 0200 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0001 2FC0
You may need to send the error log to AIX System Support Center for analysis. To copy the error log to a diskette, place a formatted diskette into the diskette drive and use the following commands:
ls /var/adm/ras/errlog | backup -ivp
To copy the error log to tape, place a tape in the drive and enter:
ls /var/adm/ras/errlog | backup -ivpf/dev/rmt0
The errlogger command allows the system administrator to record messages in the error log. Whenever you perform a maintenance activity, replace hardware, or apply a software fix, it is a good idea to record this activity in the system error log.
The following example shows the log enteries before and after a message (Error Log cleaned) was logged by an operator (using errlogger command) in the error log.
# errpt IDENTIFIER TIMESTAMP T C RESOURCE_NAME DESCRIPTION 9DBCFDEE 1109164598 T O errdemon ERROR LOGGING TURNED ON 192AC071 1109164598 T O errdemon ERROR LOGGING TURNED OFF # errlogger "Error Log cleaned" # errpt IDENTIFIER TIMESTAMP T C RESOURCE_NAME DESCRIPTION AA8AB241 1109164698 T O OPERATOR OPERATOR NOTIFICATION 9DBCFDEE 1109164598 T O errdemon ERROR LOGGING TURNED ON 192AC071 1109164598 T O errdemon ERROR LOGGING TURNED OFF
The identifier AA8AB241 in the preceding example is the message record entry with description OPEARATOR NOTIFICATION.