


 12.2 Setting Up the PPP
Control Link
12.2 Setting Up the PPP
Control Link
The following information is needed for this procedure: the IP address,
gateway, and netmask for the host.
To get this information do the following:
- Enter smitty tcpip
- Select Minimum Configuration & Startup.
- Choose the Available Network Interface, such as en0 or tr0.
- Make note of the information required.
For the purposes of this discussion, the settings you will use are:
-
Hostname
- mickey
-
Internet Address
- 9.3.1.45
-
Network Mask
- 255.255.255.0
-
Nameserver
- 9.3.1.74
-
DOMAIN Name
- itsc.austin.ibm.com
-
GATEWAY Address
- 9.3.1.74
You will need to do the following:
- Choose an unused address in the same domain: 9.3.1.46.
- Add an entry in the /etc/hosts file with the new address and hostname
for the PPP client.
- Add the PPP addresses by entering the command smitty ppp.
- Choose the option PPP IP Interfaces.
- Choose the option Add a Server Interface.
- Fill in the fields, shown in Figure 114, with
information provided previously.
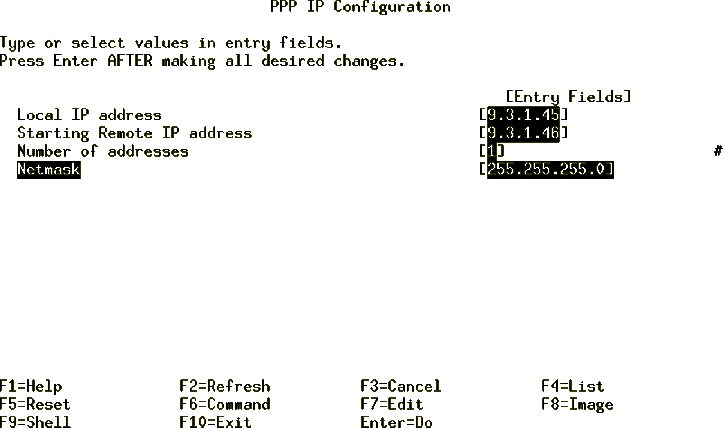
Figure 114: PPP IP Configuration
- Press Enter to add the IP Server configuration. This creates a
file entry in /etc/ppp/if_conf. The file can be viewed using the following:
# cat /etc/ppp/if_conf
interface
server
local_ip 9.3.1.45
remote_ip 9.3.1.46
netmask 255.255.255.0
- Make sure ipforwarding is
on. By default in AIX 4, ipforwarding is turned off. If you want your server to
act as a router, you need to turn ipforwarding on. Check the value of
ipforwarding with:
# no -a |grep ipf
ipfragttl = 60
ipforwarding = 0
If ipforwarding is 0, change it to 1 with:
no -o ipforwarding=1
- Because you are adding the client to the same subnet as the server, you
will want the server to respond to arp requests from other hosts in the
network, so that all traffic to the client will get routed through the hosts.
You can do this with a proxy arp.
Find the hardware address of the local adapter for the client using:
# netstat -i
Name Mtu Network Address Ipkts Ierrs Opkts Oerrs Coll
lo0 16896 link#1 203625 0 203773 0 0
lo0 16896 127 loopback 203625 0 203773 0 0
lo0 16896 ::1 203625 0 203773 0 0
en0 1500 link#2 2.60.8c.2f.47.42 712193 0 712606 0 0
en0 1500 9.3.5 goofy_en0 712193 0 712606 0 0
tr0 1492 link#3 10.0.5a.a8.3b.fa 1088842 0 769364 0 0
tr0 1492 9.3.1 goofy 1088842 0 769364 0 0
tr1 1492 link#4 10.0.5a.a8.d1.f3 1076155 0 726539 0 0
tr1 1492 9.3.4 goofy_stby 1076155 0 726539 0 0
Add an arp entry for the remote host using:
arp -s type hostname hardware address pub
where:
-
type
- The type of your network adapter. Valid types are: ether, 802.3, fddi,
802.5 (token ring).
-
hostname
- Hostname of the client.
-
hardware address
- From netstat -i. Use colon separators.
-
pub
- Indicates public and permanent.
The token ring (tr0) hardware address is used for this example.
- Verify the arp entries with an arp -a command, the output is as
follows:
goofy (9.3.1.46) at 10:0:5a:8c:3b:fa [token ring] permanent published



 12.4 Adding a PPP Login
User
12.4 Adding a PPP Login
User



 12.2 Setting Up the PPP
Control Link
12.2 Setting Up the PPP
Control Link


 12.2 Setting Up the PPP
Control Link
12.2 Setting Up the PPP
Control Link