


 2.3 Preservation
Installation
2.3 Preservation
Installation
The lppchk command verifies that files for an
installable software product (fileset) match the Software
Vital Product Data (SWVPD) database information for file
sizes, checksum values, or symbolic links.
The available flags are briefly described:
-
-c
- Performs a checksum operation on the input FileList items and verifies that
the checksum and the file size are consistent with the SWVPD database.
-
-f
- Checks that the FileList items are present and that the file size matches
the SWVPD database.
-
-l
- Verifies symbolic links for files as specified in the SWVPD database.
-
-m
- Displays three levels of information.
-
-O
- Verifies the specified parts of the program. This flag is not needed with
standalone systems because without this option all parts are verified by
default.
-
-u
- Updates the SWVPD with new checksum or size information from the system
when the system information does not match the SWVPD database. This flag sets
symbolic links that are found to be missing. This flag is valid with only the
-c or -l flag.
-
-v
- Verifies that the / (root), /usr, and /usr/share parts of the system are
valid with each other. In other words, this flag verifies that all software
products installed on the / (root) file system are also installed on the /usr
file system and, conversely, all the software products installed in the /usr
file system are also installed on the / (root) file system. You cannot specify
FileList items with this flag. This flag also verifies requisites.
| Note |
|---|
|
Only one of the -c, -f, -l, and -v flags can be specified with each use of
the lppchk command.
|
The installation of the bos.dosutil fileset is interrupted in the following
example. An example of the lppchk -v command is shown in
Figure 1 before and after the inconsistency is cleaned up:
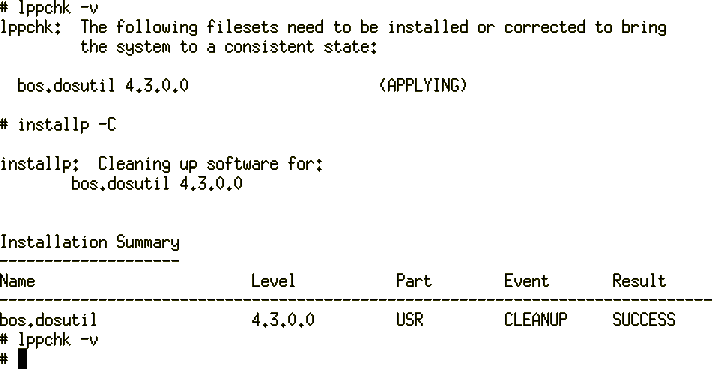
Figure 1: Sample lppchk -v Command



 2.5 The smit.log File as
the installp Command Output Log
2.5 The smit.log File as
the installp Command Output Log



 2.3 Preservation
Installation
2.3 Preservation
Installation