


 14.5 Scheduling
Run
14.5 Scheduling
RunThe /var/adm/cron/cron.allow and /var/adm/cron/cron.deny files control which users can use the crontab command. A root user can create, edit, or delete these files. Entries in these files are user login names with one name per line. A user cannot use the crontab command if one of the following is true:
If neither the cron.allow nor the cron.deny file exists, only someone with root user authority can submit a job with the crontab command.
The empty /var/adm/cron/cron.deny file has been deleted for security
reasons. To allow the people in charge of application deployment to schedule
applications to be run, a /var/adm/cron/cron.allow file is created as in
Figure 118:
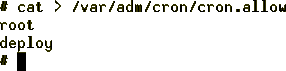
Figure 118: Creating the cron.allow File
There are also the /var/adm/cron/at.allow and /var/adm/cron/at.deny files that control which users can use the at command using the same rules as the /var/adm/cron/cron.allow and /var/adm/cron/cron.deny files.